Installation and setup of java development kit(JDK),setup android
SDK,setup eclipse IDE,setup android development tools (ADT)
plugins,create android virtual device
for Android Studio
Android Studio is the official IDE (Integrated Development Environment) for Android app development and it is based on JetBrains’ IntelliJ IDEA software. Android Studio provides many excellent features that enhance productivity when building Android apps, such as:
- A blended environment where one can develop for all Android devices
- Apply Changes to push code and resource changes to the running app without restarting the app
- A flexible Gradle-based build system
- A fast and feature-rich emulator
- GitHub and Code template integration to assist you to develop common app features and import sample code
- Extensive testing tools and frameworks
- C++ and NDK support
- Built-in support for Google Cloud Platform, making it easy to integrate Google Cloud Messaging and App Engine, and many more.
System Requirements
- Microsoft Windows 7/8/10 (32-bit or 64-bit)
- 4 GB RAM minimum, 8 GB RAM recommended (plus 1 GB for the Android Emulator)
- 2 GB of available disk space minimum, 4 GB recommended (500 MB for IDE plus 1.5 GB for Android SDK and emulator system image)
- 1280 x 800 minimum screen resolution
Installation Guide
Step 1: Head over to
this link to get the Android Studio executable or zip file.
Step 2: Click on the Download Android Studio Button.
Click on the “I have read and agree with the above terms and conditions” checkbox followed by the download button.
Click on the Save file button in the appeared prompt box and the file will start downloading.
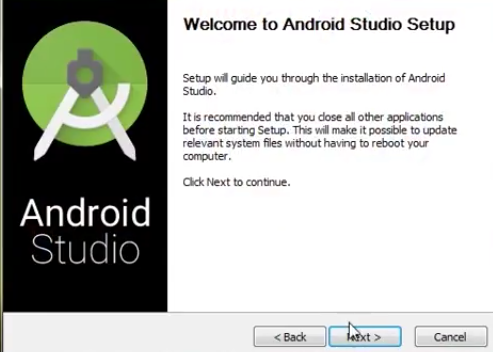
Step 3: After the downloading has finished, open the file from downloads and run it. It will prompt the following dialog box.
Click on next. In the next prompt, it’ll ask for a path for installation. Choose a path and hit next.
Step 4: It will start the installation, and once it is completed, it will be like the image shown below.
Click on next.
Step 5: Once “Finish” is clicked, it will ask whether the previous settings need to be imported [if the android studio had been installed earlier], or not. It is better to choose the ‘Don’t import Settings option’.
Click the OK button.
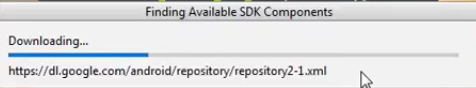
Step 6: This will start the Android Studio.
Meanwhile, it will be finding the available SDK components.
Step 7: After it has found the SDK components, it will redirect to the Welcome dialog box.
Choose Standard and click on Next. Now choose the theme, whether the Light theme or the Dark one. The light one is called the IntelliJ theme whereas the dark theme is called Darcula. Choose as required.
Click on the Next button.
Step 8: Now it is time to download the SDK components.
Click on Finish. Components begin to download let it complete.
The Android Studio has been successfully configured. Now it’s time to launch and build apps. Click on the Finish button to launch it.
Step 9: Click on Start a new Android Studio project to build a new app.
Step 10: Then, name your application in the ‘Application name‘ Text box.
By default, the application name appears as “MyApplication”. Click on “Next” after filling the Application name field, leaving the other fields to their default values.
Then select the Minimum SDK to select the operating system which must be least version to run your app, here “Jelly Bean” is made Minimum SDK, and phones and tablets with versions lower to this OS will not be able to run your apps. Click on “Next”.
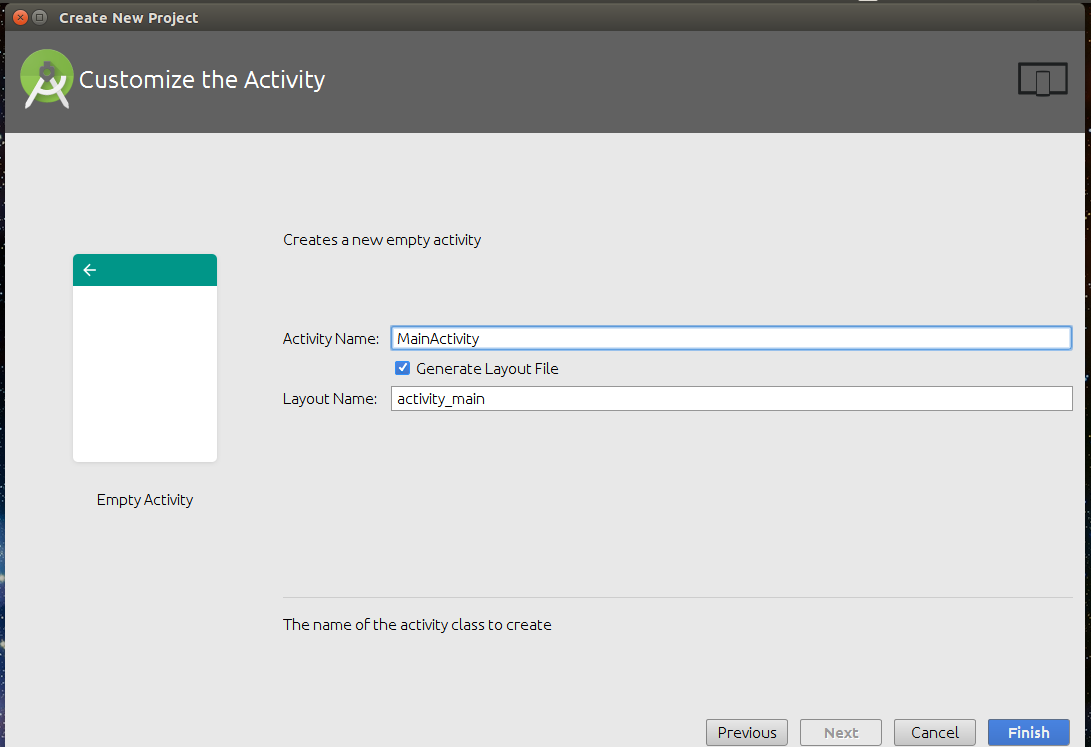
The next step is to choose the Activity to mobile. Activity in Android refers to a single screen with a user interface. For Beginners, “Empty Activity” is recommended.
Then, fill the Activity name text field. By default, “MainActivity” is filled in this text box as the name of your activity. In android studio, files are usually named in camel case. An xml file of the activity is created using the first word in the Activity name. An xml file is a file to provide functionalities of user interface for our app.
Click on “Finish”.
Then, a default app is created with all default files. And you can now start writing the application code.
Setup Android Virtual Device
To create a new AVD:
- Open the AVD Manager by clicking Tools > AVD Manager.
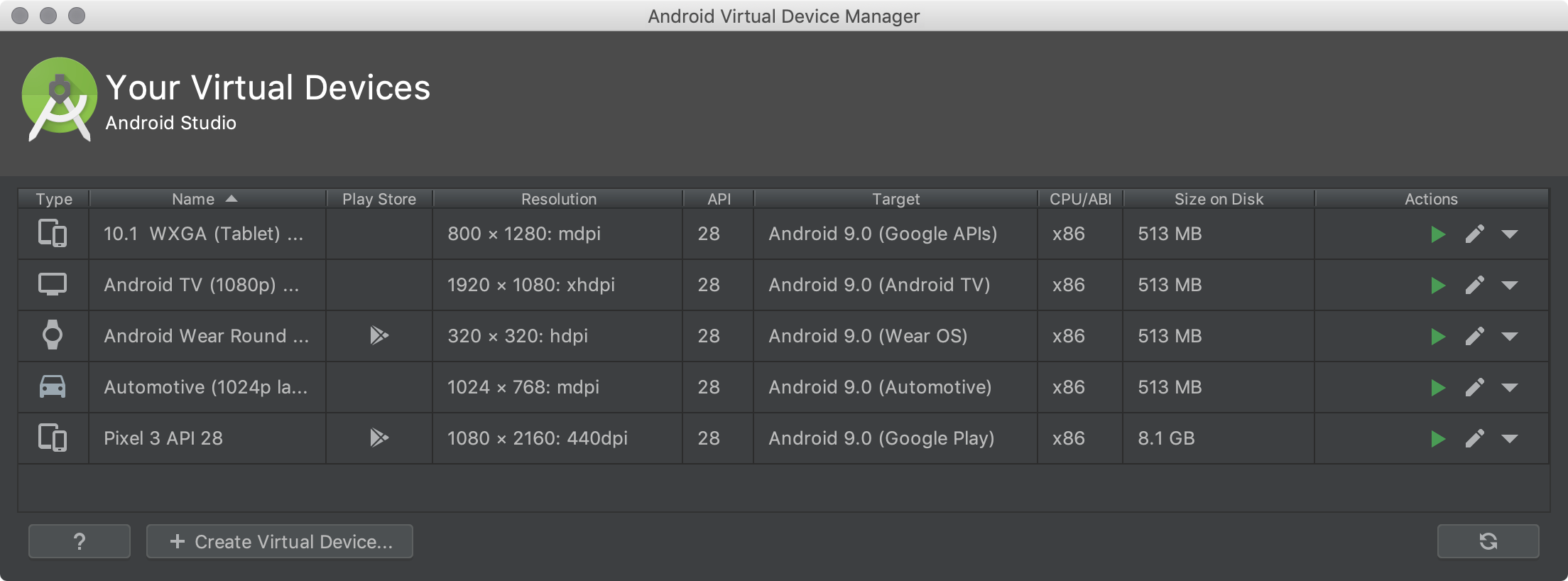
- Click Create Virtual Device, at the bottom of the AVD Manager dialog.
The Select Hardware page appears.
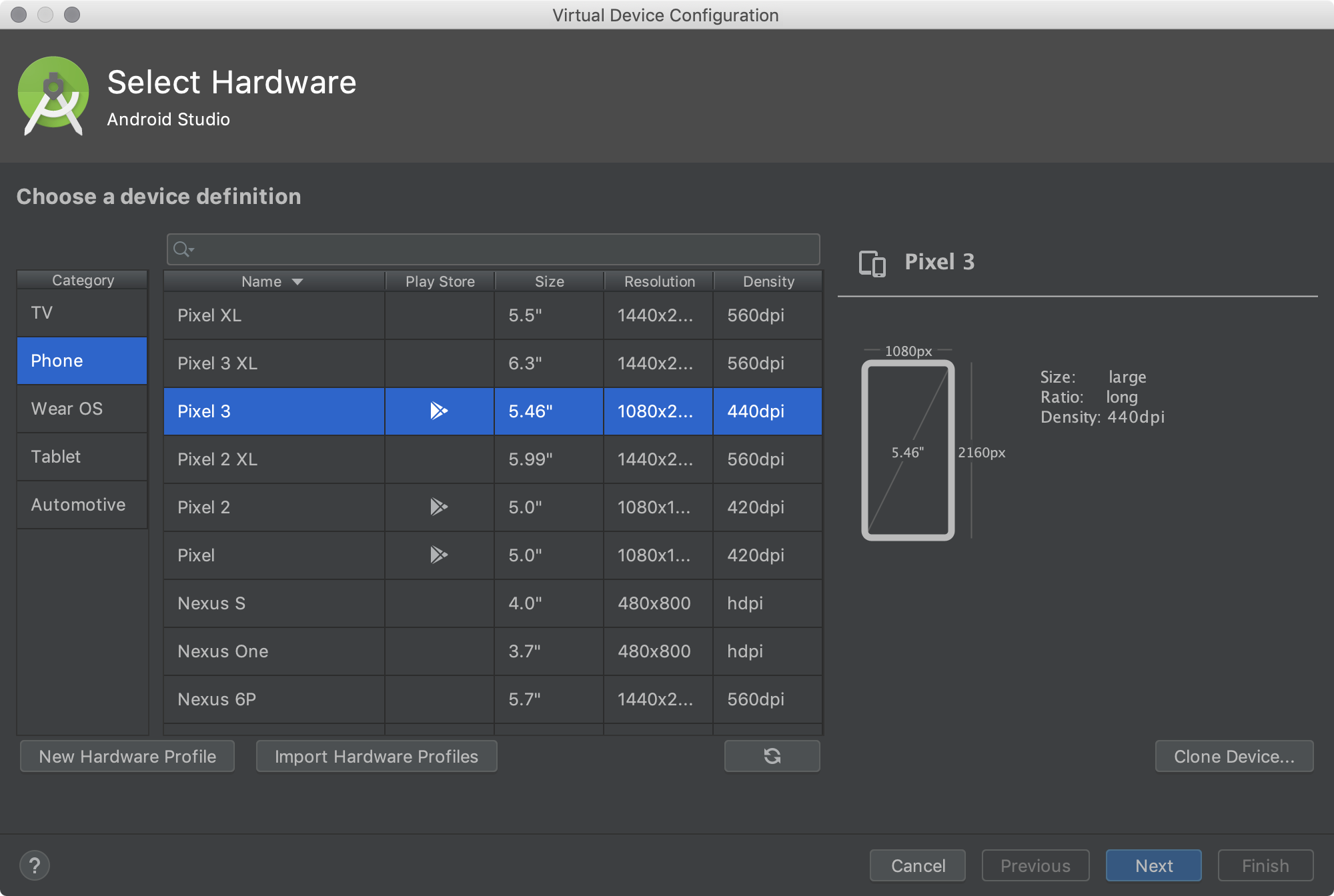
Notice that only some hardware profiles are indicated to include Play Store. This indicates that these profiles are fully CTS compliant and may use system images that include the Play Store app.
- Select a hardware profile, and then click Next.
If you don't see the hardware profile you want, you can create or import a hardware profile.
The System Image page appears.
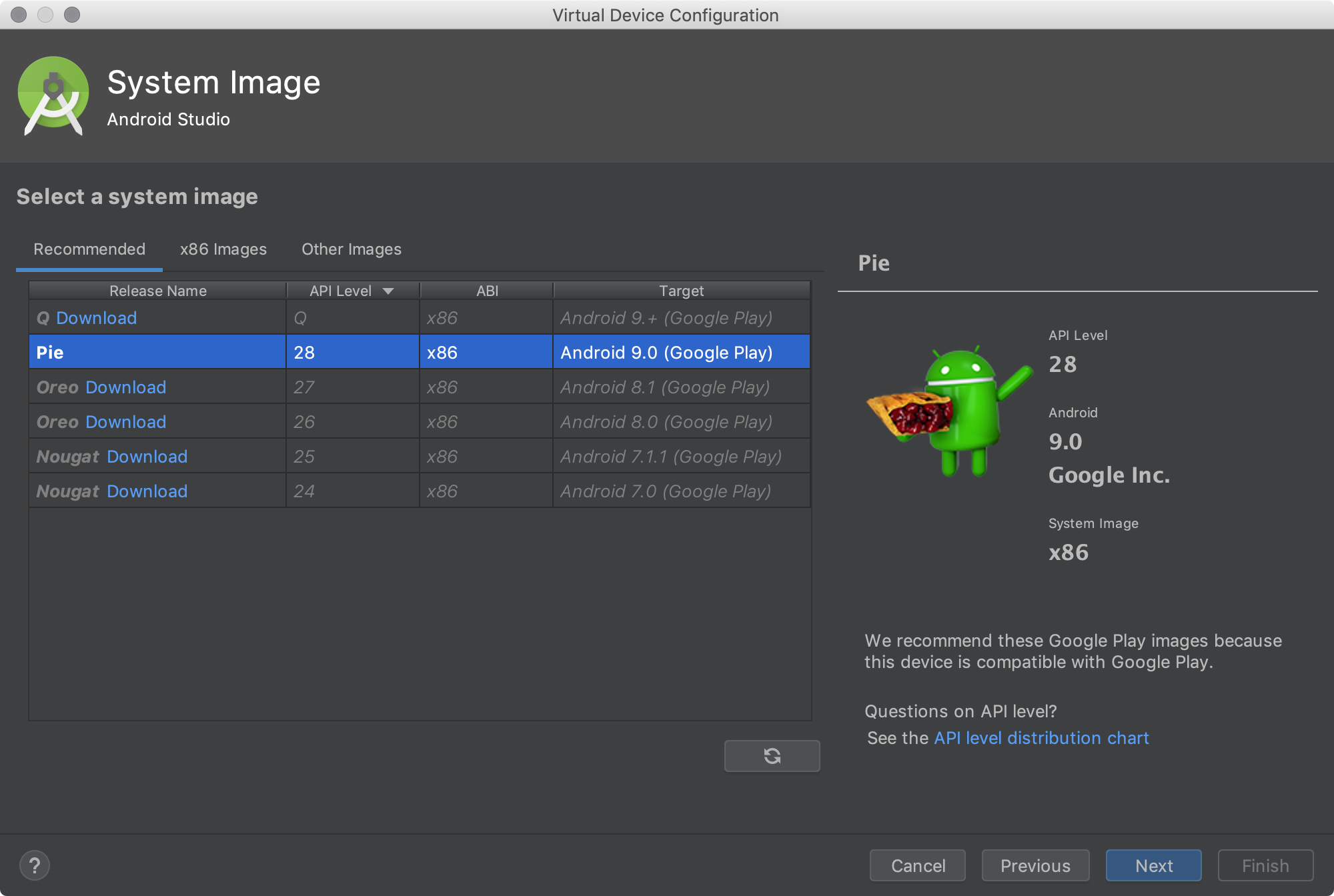
- Select the system image for a particular API level, and then click Next.
The Recommended tab lists recommended system images. The other tabs include a more complete list. The right pane describes the selected system image. x86 images run the fastest in the emulator.
If you see Download next to the system image, you need to click it to download the system image. You must be connected to the internet to download it.
The API level of the target device is important, because your app won't be able to run on a system image with an API level that's less than that required by your app, as specified in the minSdkVersion attribute of the app manifest file. For more information about the relationship between system API level and minSdkVersion, see Versioning Your Apps.
If your app declares a <uses-library> element in the manifest file, the app requires a system image in which that external library is present. If you want to run your app on an emulator, create an AVD that includes the required library. To do so, you might need to use an add-on component for the AVD platform; for example, the Google APIs add-on contains the Google Maps library.
The Verify Configuration page appears.
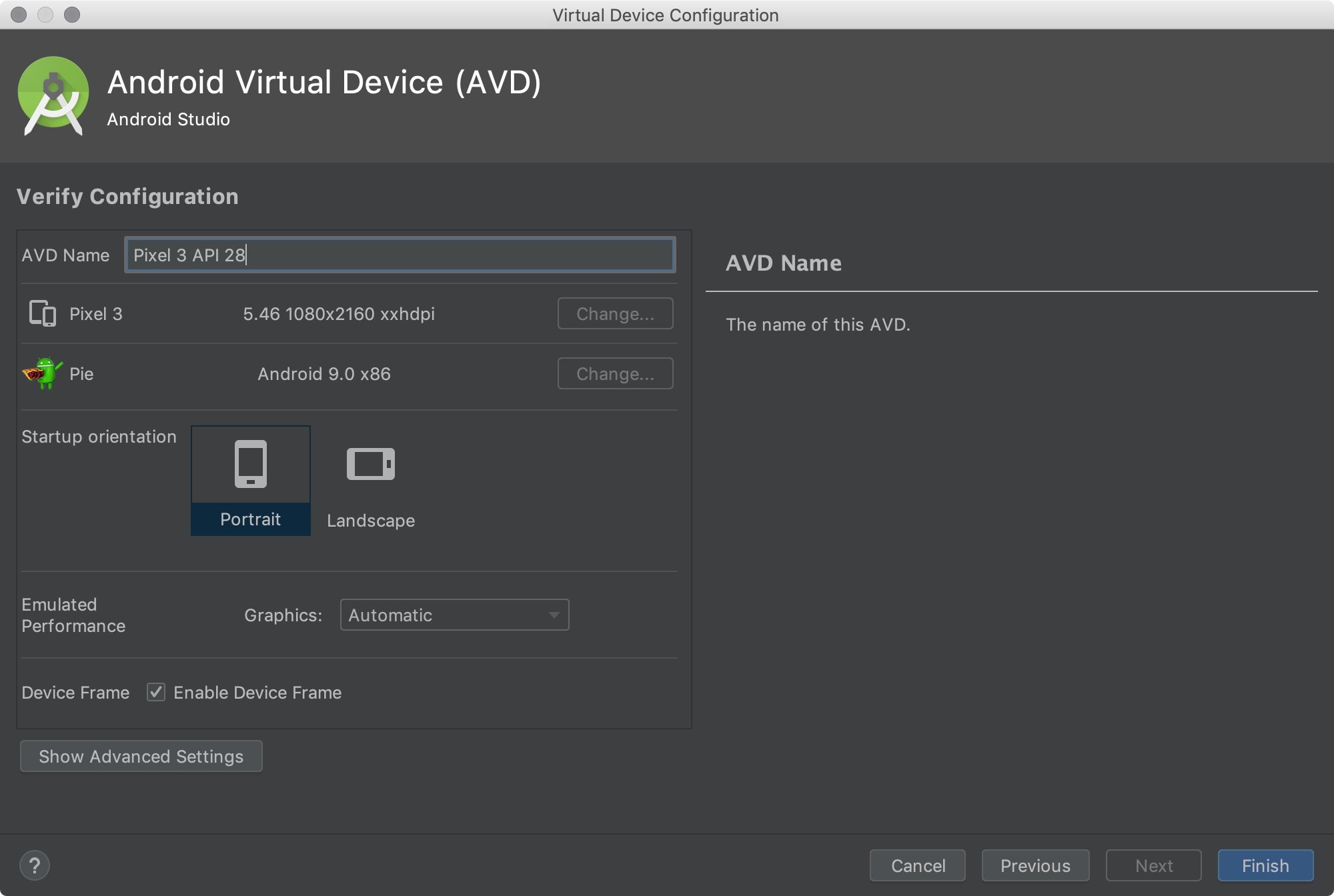
- Change AVD properties as needed, and then click Finish.
Click Show Advanced Settings to show more settings, such as the skin.
The new AVD appears in the Your Virtual Devices page or the Select Deployment Target dialog.
To create an AVD starting with a copy:
- From the Your Virtual Devices page of the AVD Manager, right-click an AVD and select Duplicate.
Or click Menu  and select Duplicate.
and select Duplicate.
The Verify Configuration page appears.
- Click Change or Previous if you need to make changes on the System Image and Select Hardware pages.
- Make your changes, and then click Finish.
The AVD appears in the Your Virtual Devices page.




![]() and select Duplicate.
and select Duplicate.













0 Comments
Post a Comment